The production process of electrical wire and cable
The production process of electrical wire and cable typically involves the following steps:
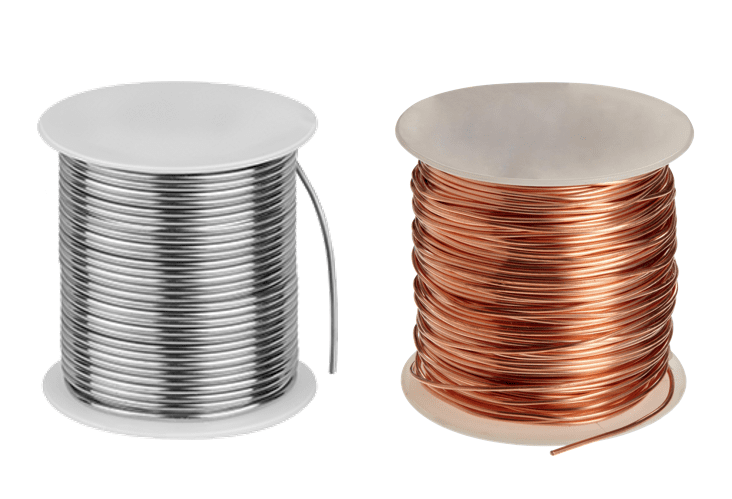
1. Wire Drawing:
In this step, copper or aluminum rods are drawn through a series of dies to reduce their diameter and form wire of the desired size.
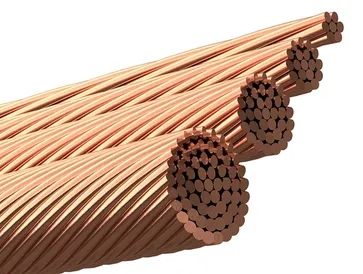
2. Stranding:
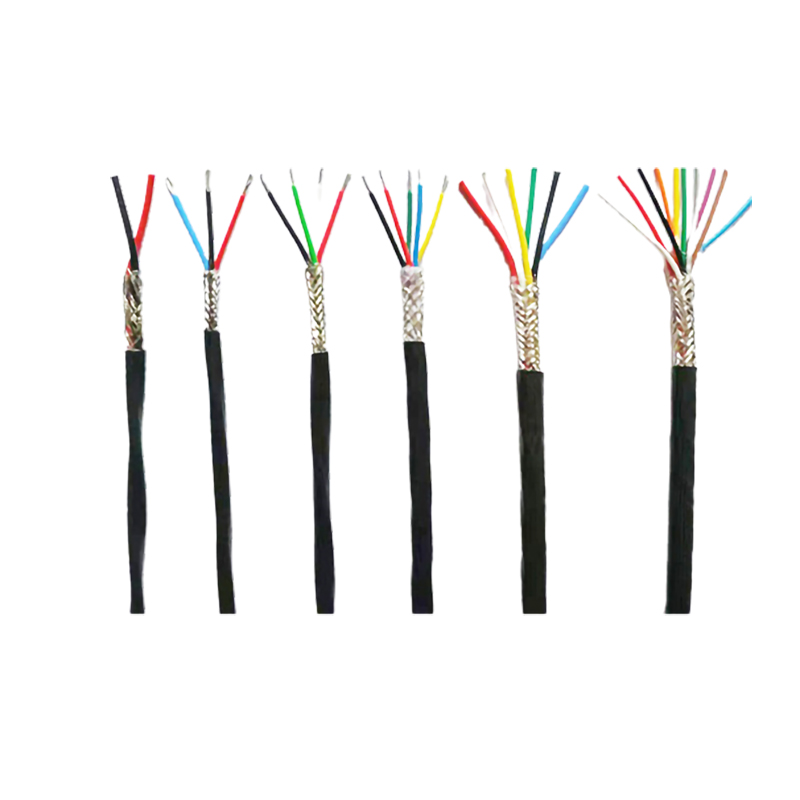
Multiple wires are combined to form a stranded conductor. This process increases flexibility and reduces electrical resistance.
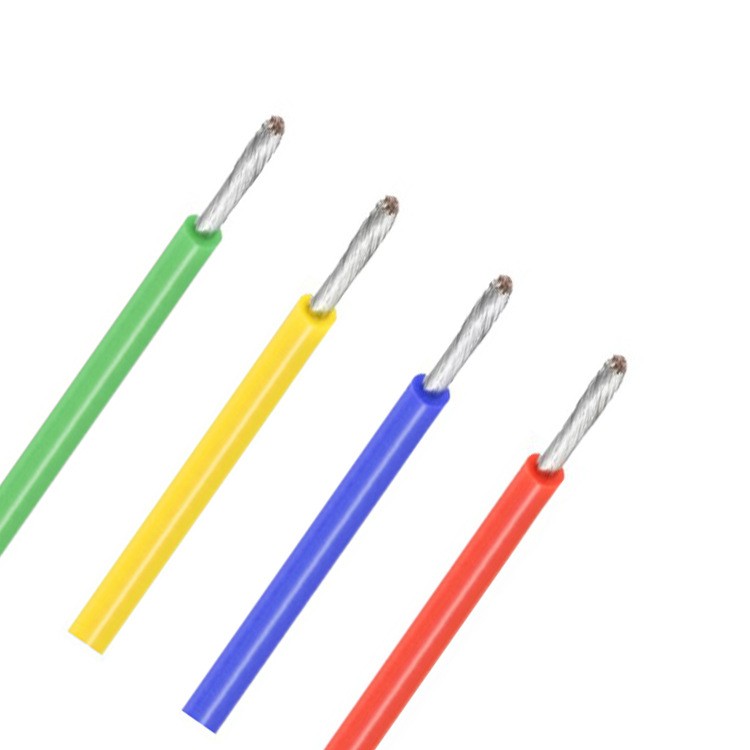
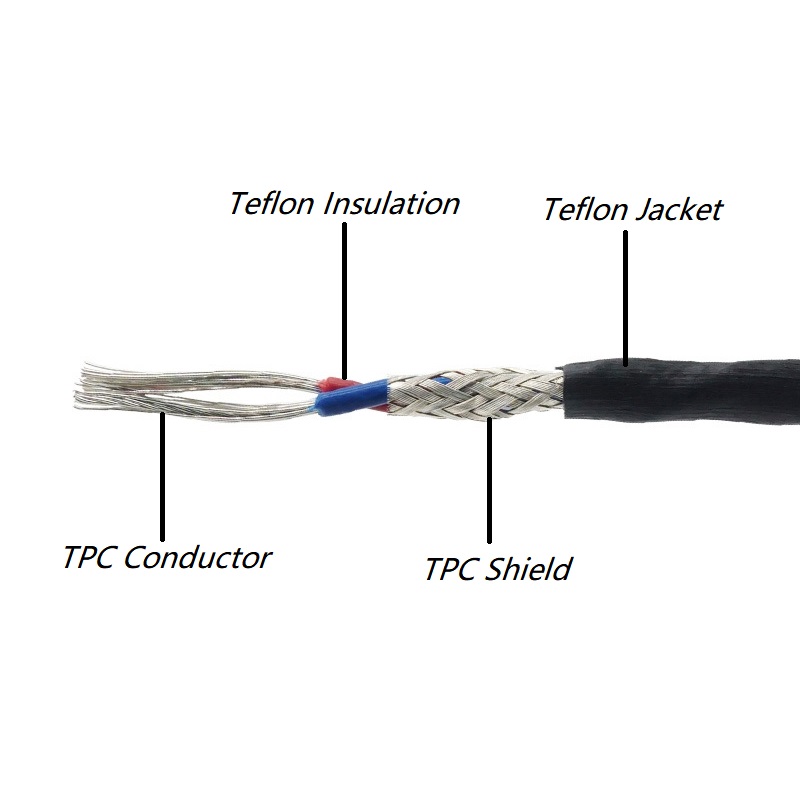
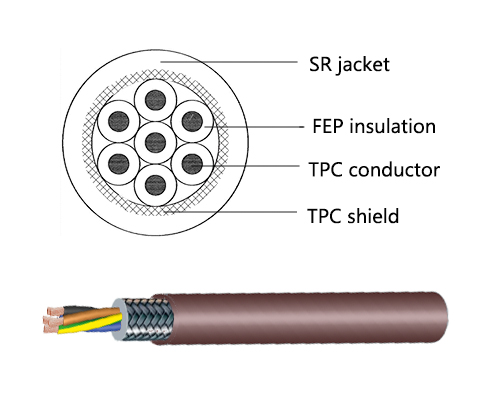
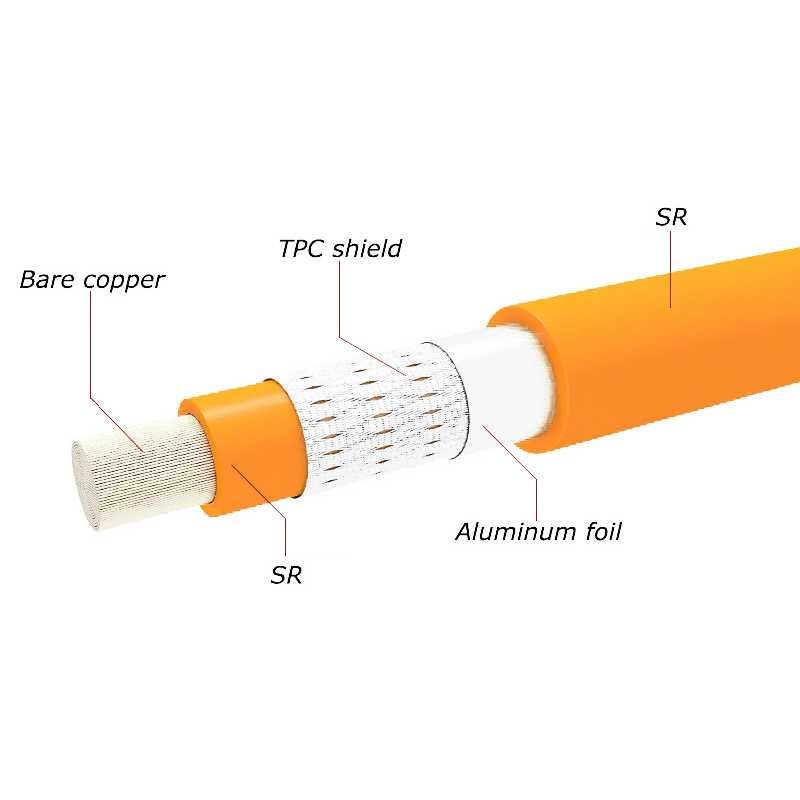
3. Insulation Extrusion:
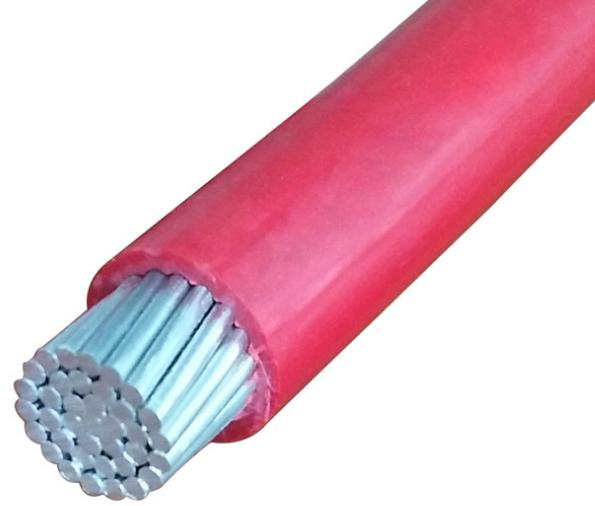
The stranded conductor is passed through an extruder, where a layer of insulating material (such as PVC, XLPE, or rubber) is applied to provide electrical insulation.
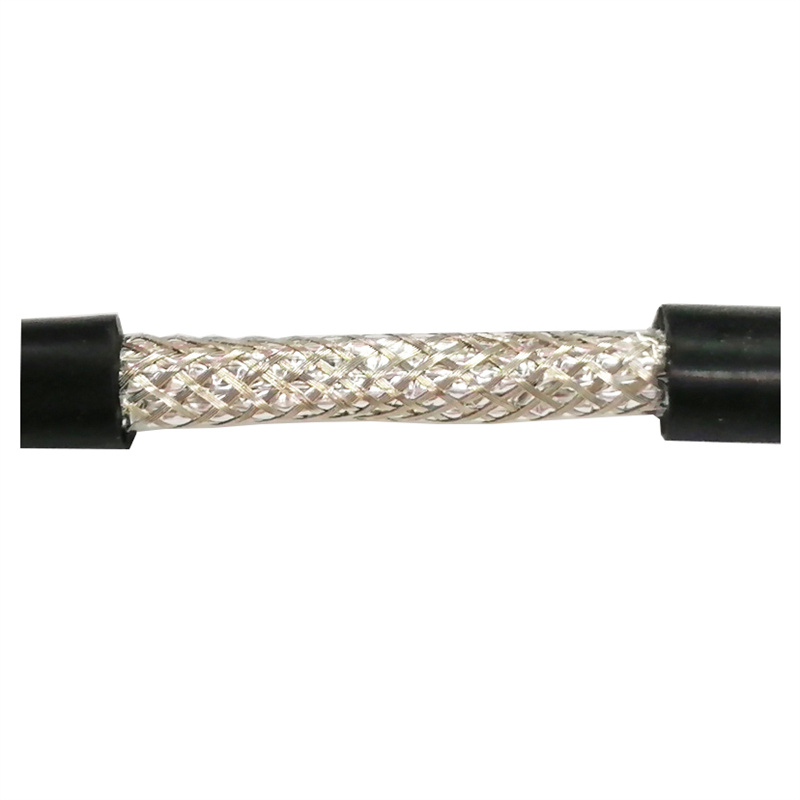
4. Shielding:
In certain cable applications, a metallic shield is applied over the insulation to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI).
5. Jacketing:
A protective outer layer, usually made of PVC, is applied to the cable to provide mechanical protection and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and sunlight.
6. Cabling:
Multiple insulated conductors or insulated pairs/triples are combined to form a cable core, which can be further twisted or laid up together.
7. Armoring (Optional):
In some applications where added mechanical protection is required, a layer of metal braid or tape may be added as an armor.
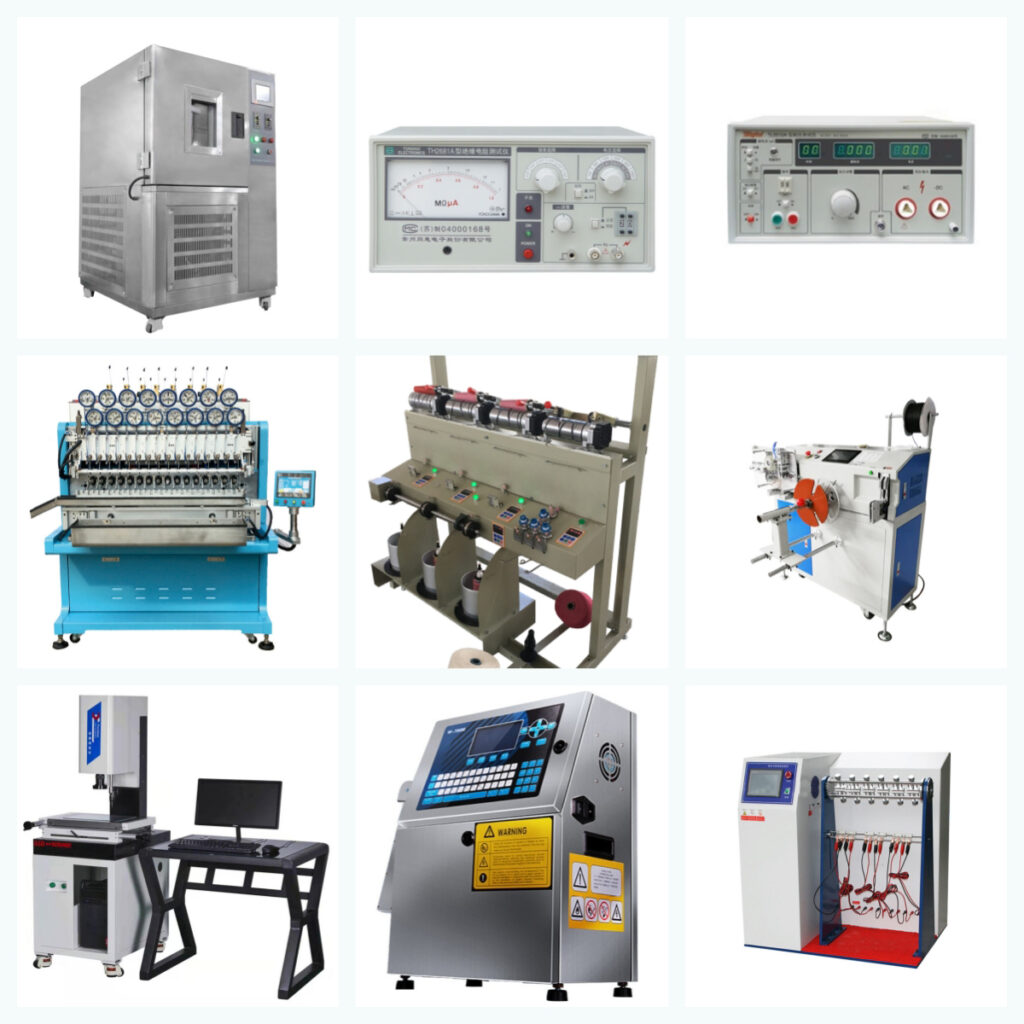
8. Testing:
Various tests are conducted on the finished cables to ensure compliance with performance and safety standards.
9. Packing and Delivery:
Once the cables pass the quality control tests, they are coiled, packed, and sent for delivery to the customers.